Shellac plays a significant yet often overlooked role in the pharmaceutical industry. Derived from the resinous secretion of the lac insect, shellac is used as a natural coating agent for tablets, capsules, and pills. Its versatility, safety, and unique properties make it an ideal choice in modern drug delivery systems.
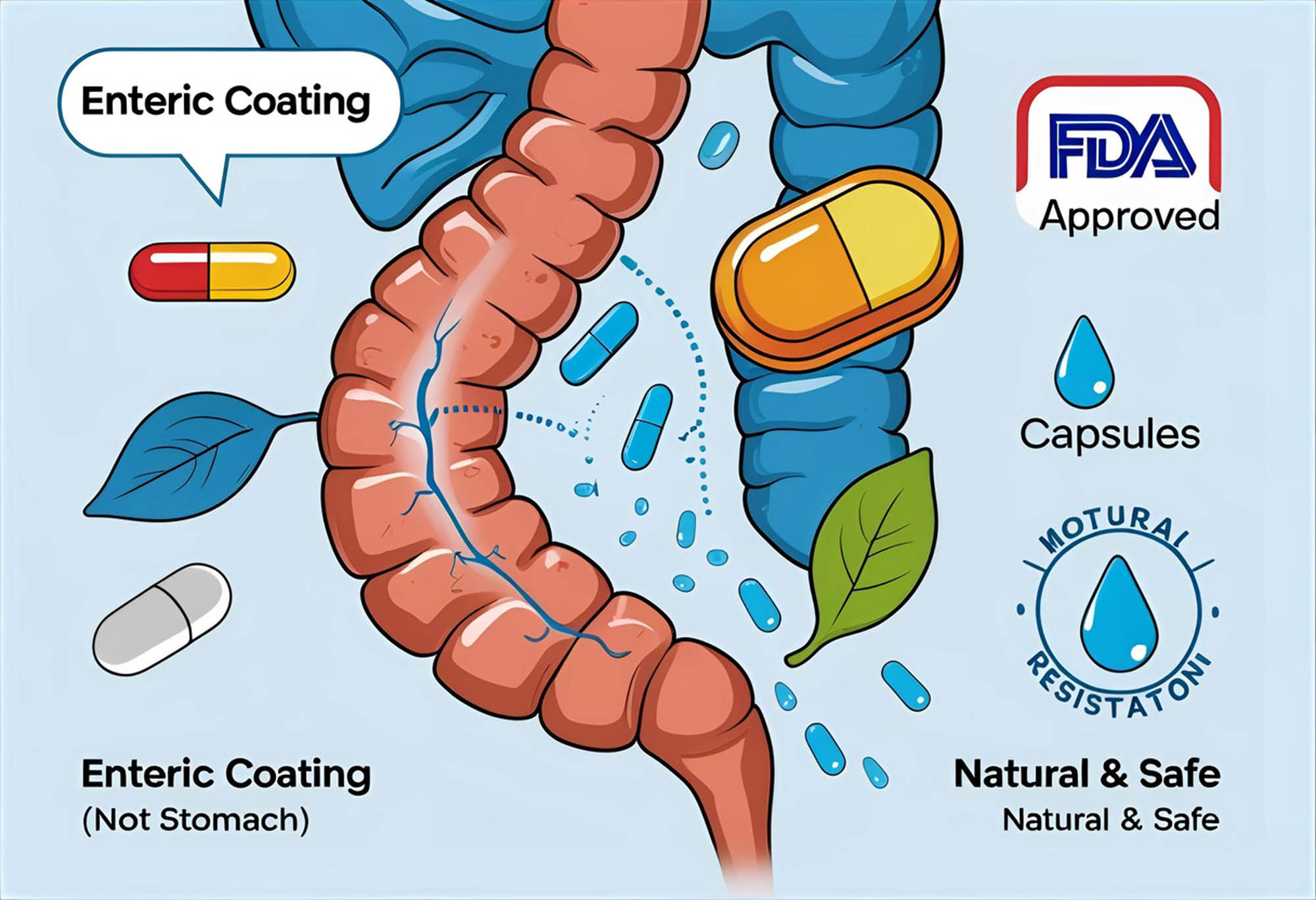
One of the primary applications of shellac in pharmaceuticals is as an enteric coating. This means it helps tablets resist stomach acid and dissolve only when they reach the intestines, ensuring that active ingredients are released at the right time and place within the digestive tract. Its natural pH-dependent solubility makes it especially effective for this purpose.
Shellac is also valued for its moisture resistance, which helps extend the shelf life of pharmaceutical products by protecting them from humidity and oxidation. Additionally, it provides a smooth, glossy finish that enhances the visual appeal and swallowability of pills.
Perhaps the most important advantage of shellac in this field is its non-toxic, hypoallergenic nature. Being a GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) substance by regulatory authorities like the FDA, it is widely accepted in pharmaceutical formulations intended for both adults and children.
In an age where consumers are more conscious of what goes into their medicine, shellac stands out as a natural, safe, and effective alternative to synthetic coatings. Its use continues to grow, not only because of its proven functionality but also because it aligns with the increasing demand for cleaner, more sustainable health solutions.